
Originally developed to reduce tremors from Parkinson’s disease, the FDA approved DBS for use in treating obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
#Stimulating the brain generator#
Discomfort in the area where the generator is located. However, VNS is controversial and rarely used. 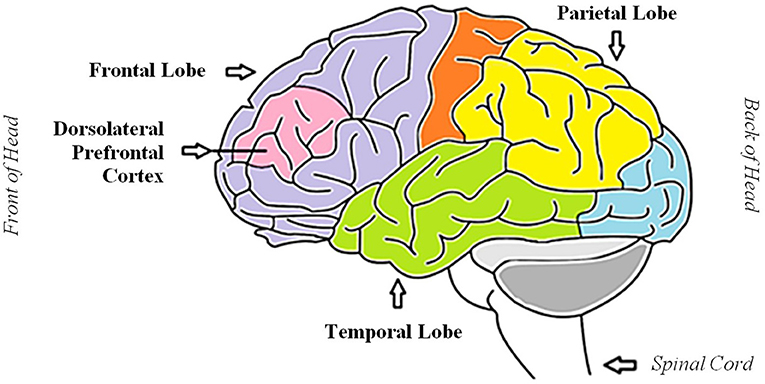
The FDA has approved VNS for treating hard-to-treat depression, depression that hasn’t improved after trying four different medications or ECT. VNS can be used to treat depression, as well as other medical conditions including epilepsy. VNS uses a pulse generator, about the size of a stopwatch, placed in the upper left side of the chest to stimulate the vagus nerve, which carries messages to parts of the brain that control mood and sleep, with electrical impulses. However, they have not been widely studied and their effectiveness remains unclear.
Seizures, if a person has a history of seizuresĮCT and TMS are the most widely used brain stimulation therapies, but there are two other options available. Muscle contractions or tingling in the face or the jaw. Side effects of TMS are usually mild and may include: It also cannot be used if a person has a pacemaker or any metal objects in their head. TMS should not be used to treat anyone experiencing depression with psychosis or bipolar disorder or having a high risk of suicide. Several sessions generally are required over a period of weeks. Unlike ECT, TMS does not require the use of anesthesia and person will remain awake during the treatment. TMS treatments will last about 40 minutes. The doctor performing the treatment will determine the amount of magnetic energy needed during the first treatment session. With TMS, a large electromagnetic coil is placed on a person’s forehead and short pulses are directed into an area of the brain believed to control moods. TMS is a procedure that creates magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of depression. Memory loss, which can range from forgetting conversations or events right before and after a treatment, forgetting things from weeks or months before treatment, and less commonly, from years before. Confusion following treatment, which may last a few minutes or hours. Physical effects, such as headaches, muscle pain, nausea. This is followed by additional treatments and in some cases “maintenance ECT” on a less frequent basis, such as once a month or once a year. Most people have four to six treatments before major improvement is seen. They are able to resume normal activity in about an hour. People are asleep during the procedure and wake up 5-10 minutes after it has finished. When it was first used in the 1940s, it was very primitive. Once called electroshock therapy, ECT still has many negative associations. In some cases of treatment resistant bipolar disorder, ECT may be considered as a treatment option. 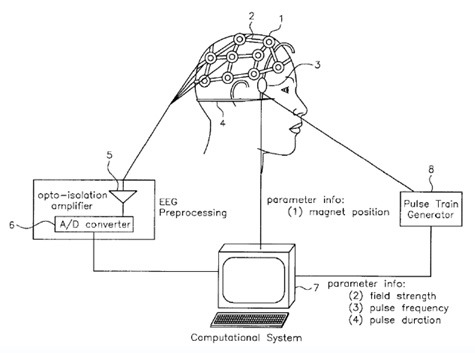
It is most often used to treat severe depression and depression with psychosis that has not responded to medications. This results in a brief, controlled seizure that affects neurons and chemicals in the brain. Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)ĮCT is a procedure where controlled electric currents are passed through the brain while the person is under general anesthesia. Brain stimulation therapies involve stimulating or touching the brain directly with electricity, magnets or implants. A psychiatrist might suggest electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or other forms of brain stimulation. When treatments such as medication and therapy aren’t able to relieve the symptoms of depression or another mental health condition, there are other options available. Weight Gain Related to Psychiatric TreatmentsĮCT, TMS and Other Brain Stimulation Therapies What to Avoid with Psychiatric Medications Methylphenidate or Dexmethylphenidate (Concerta, Ritalin and others)






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
